Explore Aerial Thermal Imaging diverse applications in agriculture, construction, and more. Unlock efficiency and insights across industries with this cutting-edge technology.
Aerial thermal imaging has emerged as a valuable instrument across many sectors as it can gather thermal data from many vantage points.
In different industrial settings, thermal imaging has played a vital role as the component that helps to maintain effective strategies.
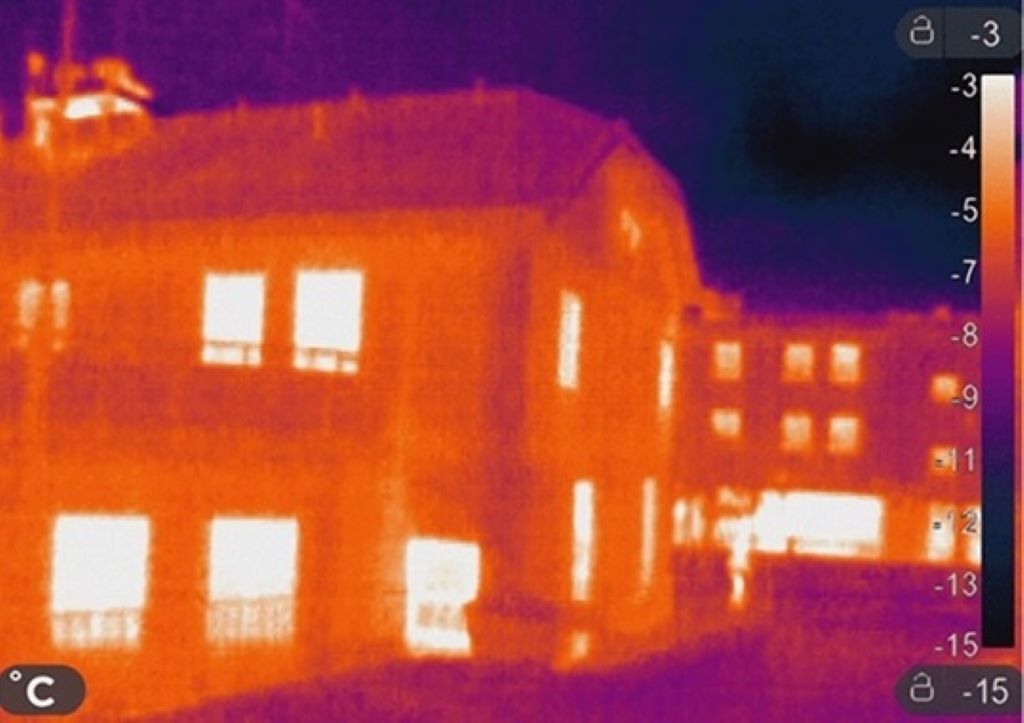

The most useful nature of thermal imaging is its thermal patterns which help in knowing any problem or malfuntions of any operation by using thermal imaging to ensure safety.
This versatility of technology has helped many industries across many countries to make their working experience effective and smooth.
It provides sound and reliable thermal patterns which helps in the quick identification of the issues, which in the short term helps to optimize the efficiency and safety protocols by the staff members.
Understanding Aerial Thermal Imaging
Aerial thermal imaging is commonly known as a thermogram as it helps to understand the visual heat of the product with the use of thermal procedures. The thermal images are used in a specialized way to recognize infrared lights from any object.
It is crucial to know that thermal images are different from conventional photographs as they only show natural images.
In essence, a thermal image can be defined as the diverse radiation that an object emits when under pressure or heat, in contrast, a traditional photo can only capture visible light that is reflected by any object.
To understand the thermal images in great depth you need to know about the color palette of heat and what each color means for the temperature of an object.
For example, different shades of blue usually means it signify the color is cool in contrast to red which shows an object is warm or in a heated state.
A thermal image serves as a temperature guide for many surveyed areas, spotlighting the regions that have high or low temperatures and helping to know more about the thermal geosphere.
The major underlying principle that helps to understand both straightforward methods is that: every object emits infrared energy at some degree related to its temperature.
Although it is not visible to the human eye, this form of energy can be very important for visually representing the thermal imaging system.
Aerial Thermal Imaging Applications Across Industries
Aerial thermal imaging works by detecting the infrared light that objects release. Detecting fluctuations in heat allows it to produce comprehensive thermal maps.
This procedure makes use of both advanced technology and infrared imaging methods. Some of the uses of Aerial thermal imaging across industries are given below:
Agriculture Industry: Enhancing Crop Management
Thermal imaging is a handy technique in agriculture we use to strengthen different types of crops. It helps us grow stronger plants. We also use it with animals. It gives us clues about how they are doing and more. Over time, thermal imaging and special software for it became very important in farming.
It gives us steady info about how heat is spread out. This lets us study the current conditions in real time, whether we do it straight from the field or from up in the air.
Employed within industrial animal husbandry, this mode of measurement is instrumental in the early detection of maladies and the acquisition of comprehensive health-related information about the animals. We even use cameras that can see heat in raising animals.
In plant condition monitoring, called precision farming, measuring plant transpiration is key. Like other plant research, leaf temperature gets measured to understand the plant’s water balance.
The goal here is to control growth, optimize yields, and make irrigation plans to meet specific needs. It also helps identify plant diseases and pest infestations.
Transpiration depends on external factors like wind, temperature, humidity, and the plant’s surface properties. When pests or diseases afflict a leaf, its water movement changes. Infrared cameras can quantify these shifts via temperature changes.
Construction And Building Industry: Ensuring Safety And Reliability
Using thermal imaging in construction surged in the 1970s amid an energy crisis. This began by examining how well buildings retained heat. Drones now enable efficient large-scale inspection. Industrial inspection has mostly been done by drone thermal imaging to help effectiveness.
In contemporary times, the significance of thermal imaging drones has been accentuated, propelled further by the challenges posed by climate change and the imperative to curtail the depletion of natural resources.
Thermal cameras help measure temperature. They play an important role in doing surveys and inspections, especially on roofs, focusing on flat roofs.
They are useful because they can show where water gets into the roof area. Water stands out because it holds heat differently. Using aerial thermal imaging makes site surveys quicker. It lets construction professionals spot potential problems and complete inspections quickly.
This means projects can be done more quickly and have better overall quality. With energy conservation, infrared thermography is one of the best ways to find areas where buildings lose energy.
Thermal imaging maps energy released from objects by detecting radiance levels. For search and research, speed and accuracy are vital. Advanced technology is crucial for success. A key innovation is aerial thermal imaging
Search And Rescue: Swift And Effective Response
Aerial thermal imaging on drones is transformative. Spotting heat signatures efficiently locates missing people, even in rough terrain.
Its capacity traces energy dispersion through radiance detection. In rescue, pace and precision are paramount. Cutting-edge tools critically enable triumph. Thermal aerial imaging is an important new technology.
Drone thermal imaging radically changes search and rescue. Discerning heat signatures readily finds the lost amid harsh lands. In disasters, this technology assists emergency services. It examines damaged areas, highlighting those needing immediate help.
At night, it enables search teams to navigate and locate targets in total darkness. When lost in the wilderness, it quickly finds people to accelerate rescue.
They analyze thermal data in real-time, uncovering distress patterns. This not only expedites the search endeavors but also minimizes the peril of overlooking crucial details.
Though powerful, aerial thermal imaging faces difficulties. Fog or heavy rain can reduce its effectiveness. Still, ongoing research tries to address these issues, improving performance in varied, tough settings.
Energy, Gas, Mining & Oil Industry: Safeguarding
From searching for reserves to transporting and processing, thermal cameras aid players across oil and gas.
Thermal imaging emerges as a backbone, rendering the workplace not only safer but also more lucrative and ecologically sustainable.
Aerial thermal imaging, serving as a vantage point, offers a comprehensive overview of energy infrastructure. This expansive purview enables the early detection of potential issues in power lines, transformers, and substations.
Such a proactive stance not only mitigates downtime but also curtails the peril of costly equipment failures. Within the gas industry, the intricate networks of pipelines assume a role of paramount significance.
Aerial thermography sensed it first, exposing leaks or abnormalities on these pipelines in advance. This allows for quick action to avoid hazards with certainty. In the world of specific infrared cameras, adding OGI is a game changer.
This technology detects the presence of methane, hydrocarbons, and other gases during equipment or pipeline inspection.
These wonders of infrared technology provide a non-contact way of identifying safety and production problems, especially in places that cannot be reached or seen easily.
The mining industry uses aerial thermal imaging to monitor mine integrity and detect zones prone to seismic activity. This results in preventive maintenance measures being taken that create a secure environment for miners’ work
Why Choose Upload Media Services For Aerial Thermal Imaging In Australia?
We offer our services to businesses, organizations, and individuals alike to take amazing aerial images and videos for various reasons including Marketing and advertising, Real estate, Construction, Agriculture, Industries, and Emergency or rescue.
Our commitment is to give the best possible aerial media production services to our clients.
Our experienced pilots-cum-photographers are certified by CASA and they have been in the industry for years. We use ultra-modern equipment that ensures our clients get the best results possible.
- Aerial Photography
- Aerial Videography
- 360° Aerial Photography
- Thermal Imaging
- Drone Mapping
- Drone Inspection
How Can Upload Media Services Help You In Aerial Thermal Imaging In Australia?
We are providing the finest quality of services concerning aerial thermal imaging. Our team of experienced pilots and photographers are CASA certified and have years of experience in the industry. We employ advanced techniques and equipment to ensure that you receive nothing but the best. Do not go for anything else when you can have the best! Call us right away!
FAQS On Aerial Thermal Imaging
What Are The Two Types Of Thermal Imaging?
- Cooled IR Sensors
- Uncooled IR Sensors
Is There A Difference Between Infrared And Thermal Imaging?
While infrared uses short-wave infrared light to illuminate an area of interest; however, thermal imaging systems rely on mid- or long-wavelength IR energy.
How Much Does A Thermal Camera Drone Cost?
The price of a thermal camera depends on the brand name, model, features, and resolution it has. Nevertheless, drone thermal cameras can be priced from 2000$ going up to 15000$ and above.
What Software Are Used In Aerial Thermal Imaging
- FLIR Thermal Studio
- DJI terra
- Pix4Dmapper
- Open source software
Can You See In The Dark With Thermal Imaging?
Yes, thermal imaging instruments find heat radiations from all objects even in dark conditions. Therefore, you can see in the dark.